
 |
|||||||
Techniques for Surgical Simulations |
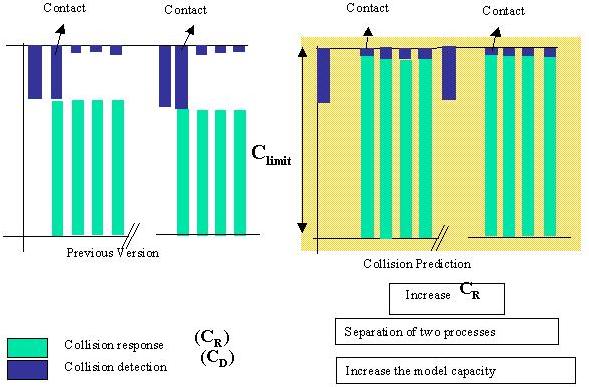
Multi-Rate Rendering: The required force update rate for stable real time interaction in a surgical simulation is very high. Majority of force feedback devices have at least a few hundred Hz update rates, which is comparably larger than the visual update rate. There is large difference between the update rate of the devices and the update rate of our scene ensuring physically realistic behavior. Consequently, we should consider a multi-rate rendering scheme when the various modalities are involved in the system. We have developed an interpolation or extrapolation scheme to generate continuous forces for force-feedback devices. Collision prediction: In rendering of deformable object haptically and visually in real time, collision detection and collision response from the model are the dominating tasks in the computation. Because two tasks are both computationally expensive and need high update rates, two tasks have a trade-off relationship that limits the performance of whole system. The collision prediction removes this trade-off relationship by separating two tasks. We have developed a collision detection scheme exploiting the fact that the userís hands holding the force-feedback devices have low frequency motion (of the order of 10Hz or less) compared to the sampling frequency of the system (100 to 1000Hz), the approach direction of the tools can be computed from the trajectories. Kim J, De S, and Srinivasan MA (2002), Computationally Efficient Techniques
for Real Time Surgical Simulation with Force Feedback, IEEE Virtual Reality
Conference. |
| Last Updated: May 8, 2002 1:45 PM | Comments: David Schloerb |